Application of Cooling Towers for Free Cooling
Energy costs and operating efficiency have gained considerable importance in the minds of many building owners and plant operators in recent years. Current prospects for future prices of energy resources suggest that these issues will become even more urgent as environmental concerns and the high cost of money exert an ever greater impact on building design and operation.
White Rust and Galvanized Cooling Towers
Factory assembled cooling towers have been manufactured from "heavy mill galvanized" (HMG) steel for many years. HMG steel is continuously hot dip coated with protective zinc at the steel processing mill. The steel is treated subsequent to coating with a chromate rinse to initially passivate the zinc surface, providing for protection during storage, fabrication and initial operation from "wet storage stain".
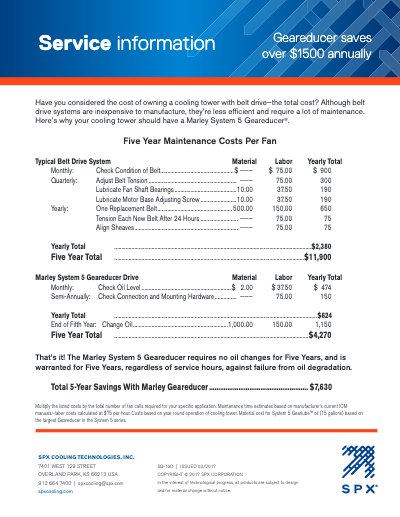
Service Information – Marley Geareducer Savings
Have you considered the cost of owning a cooling tower with belt drive—the total cost? Although belt drive systems are inexpensive to manufacture, they're less efficient and require a lot of maintenance.
Service Information – Disposal of Treated Wood
The disposal of waste wood from new tower construction, tower reconstruction or demolition may be a regulated activity, depending on the nature of the wood involved and the circumstances of disposal.
Selection of Corrosion Resistant Materials for Cooling Towers
Evaporative cooling towers expose materials to a uniquely difficult environment where corrosion poses exceptional challenges. Every cooling tower must endure the combined corrosive effects of uncertain water chemistry, high temperatures, constant saturation and continuous natural aeration. In addition, many cooling towers must also contend with potentially harmful agents in their circulating water as well as a variety of airborne pollutants such as sulfur oxides and acid rain.
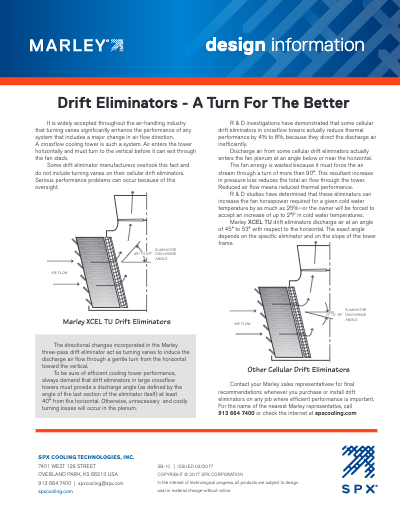
Service Information – Drift Eliminators (A Turn For The Better)
In a crossflow cooling tower, air enters the tower horizontally and must turn to the vertical before it can exit through the fan stack. Some drift eliminator manufacturers overlook this fact and do not include turning vanes on their cellular drift eliminators.